Intraventricular Drugs Delivery - Intracerebral Baclofen Pump - Intraventricular Baclofen Pump
Baclofen is a drug option used for the treatment of spasticity and some dystonias, especially secondary dystonias and dystonia-spastic. When administered orally or by gastrostomy, it has low absorption and arrives very little where it should, which is inside the CSF, for its action on the nervous system. If oral baclofen was not sufficient to improve its spasticity or the side effects were limiting, preventing oral dose escalation, the intrathecal route could instead be tested as a therapeutic option, at the discretion of the functional neurosurgeon. Intrathecal baclofen trial is suggested prior to implantation of baclofen pump. For selected patients, such as patients with cerebral palsy classified as GMFCS IV or GMFCS V, with predominance of dystonia-spastic, one option is the implantation of intraventricular baclofen pump, that is, with the catheter infusing baclofen directly into the cerebral ventricle.
What is the difference of Baclofen being infused into the intrathecal and intraventricular (intracerebral) routes?
When an oral medication or gastrostomy is used to act directly on the central nervous system, this medication must be absorbed in the digestive tract, fall into the bloodstream, cross the blood-brain barrier, and then be released into the cerebrospinal fluid , where it will reach its target of action. However, many medications go far beyond the blood-brain barrier and high blood concentrations are required to achieve small concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid. With direct intrathecal infusion of baclofen, the concentrations reached in the CSF are much higher than the concentrations of the same medication even when used at the maximum oral dose. In the case of baclofen, it is estimated that its concentration around the marrow is 40 times higher than the maximum oral dose. If the doses were equivalent, ie the same oral dose was injected directly into the cerebrospinal fluid, the potency would be greater than 1000 times when the intrathecal route was used. The highest concentration of baclofen is around the tip of the catheter where it is being infused. Although in the medical literature there are controversies about the best location for baclofen pump catheter placement, Dr. Monaco has personal experience that makes him position the catheter in optimized positions for each patient. It is known that for a baclofen distribution to occur within a specific region in the brainstem, the best position of the catheter is within the cerebral ventricle, with apparent superior action to intrathecal for cases of dystonia. In parallel to this, patients with severe dystonia-spastic secondary to cerebral palsy may present scoliosis in up to 78% of cases, and the intrathecal catheter inserted by usual route (lumbar spine) is incompatible with spinal surgery, since there would be great risk of catheter injury, with acute abstinence from intrathecal baclofen, which can lead to serious consequences.
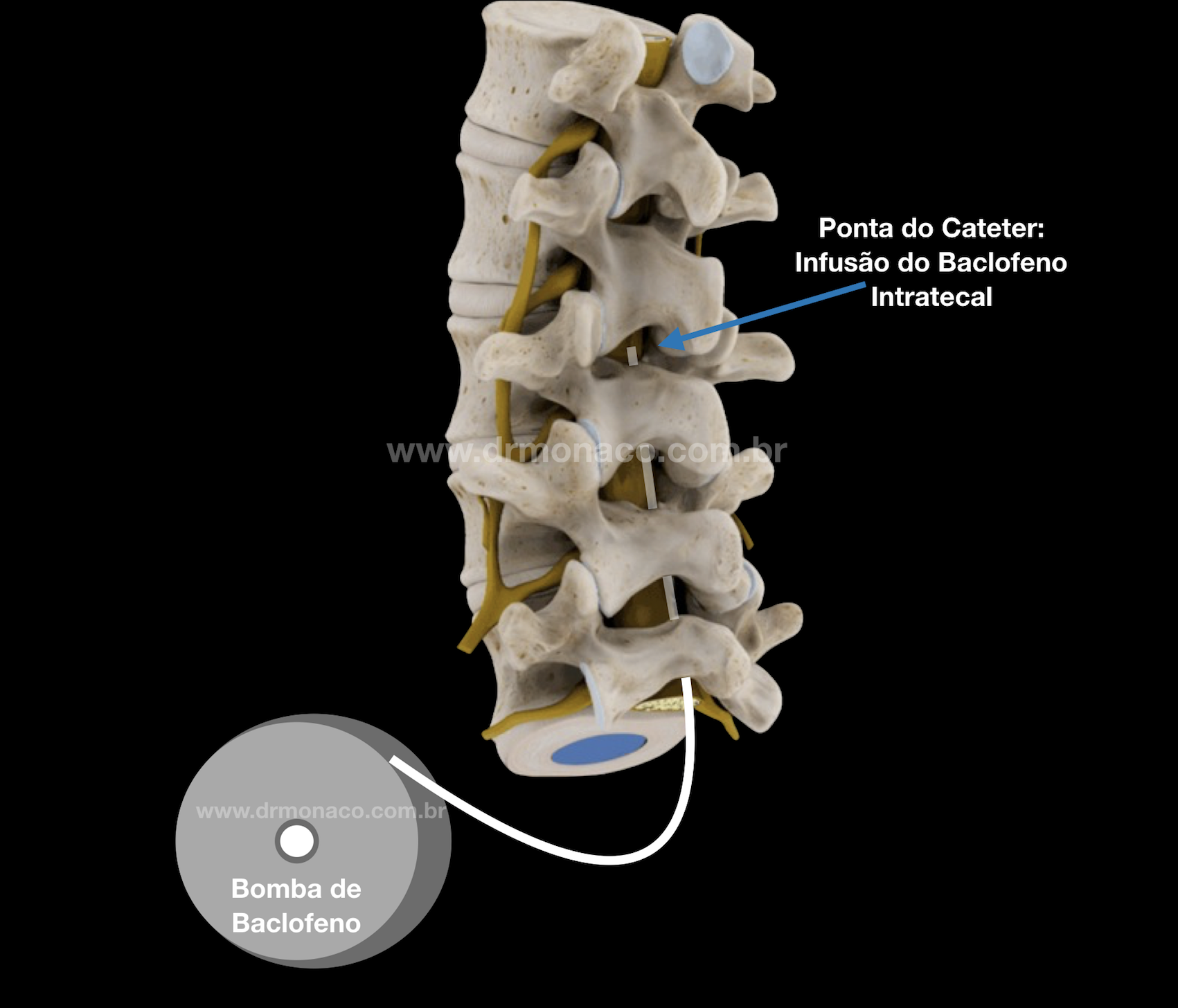
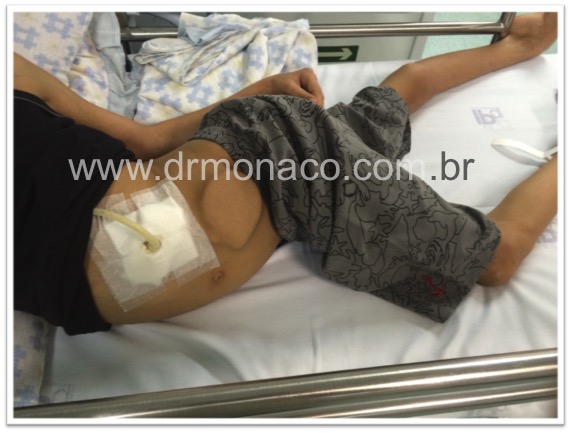
Intrathecal baclofen pump: The drug reservoir is usually implanted in the belly region, below the skin, and it leaves a catheter that takes the medication directly to the cerebrospinal fluid, distributing it in the central nervous system.
When Dr. Monaco indicates intraventricular baclofen pump?
Dr. Monaco prefers whenever possible to perform the so-called ablative surgeries (you can read more about selective dorsal rhizotomy, DREZ, myelotomy among others). In some cases, ablative surgery may bring about an improvement in spasticity, but with worsening quality of life or loss of function. For these cases, Dr. Monaco prefers neuromodulatory techniques, such as intrathecal drug infusion or spinal stimulation or brain stimulation. When the patient with cerebral palsy or equivalent picture presents an intense limitation of their daily activities due to spastic dystonia, painful pictures, progressive worsening of posture and tendency to present fixed deformities, even with clinical treatment being applied, it is time to consider surgical procedures for improvement. In some patients with GMFCS IV and V with dystonic or choreo-athetoid predominance, Dr. Monaco has indicated intraventricular baclofen pump. For the implantation of the catheter into the ventricle, it is recommended to use neuronavigation methods, such as a neuronavigator or stereotactic for implantation with perfection. It is not necessary to "open" the head to implant the catheter inside the brain, just a small cut with a small hole in the skull for its correct insertion. Small haircut over the incision area may be necessary.
What infusion pumps are available in Brazil?
Currently we have only one model of programmable electronic infusion pump in Brazil, called Medtronic's Synchromed II. A competing electronic pump, called Prometra II of the Flowonix brand, is awaiting authorization from ANVISA to be distributed in the country. One option for electronic pumps is gas-flow continuous pumps, such as the German Tricumed, available in Brazil in adult and pediatric sizes. Since titration and mode of infusion of baclofen vary, the programmable electronic infusion pumps are best suited for infusion.
What are the complications of baclofen pump implant surgery?
The complications decrease in the hands of experienced teams, as well as their performance in hospitals where the procedure is performed routinely. The most common complications are: infection, hematoma, postoperative pain, cerebrospinal fluid leakage, pump displacement, medication intoxication, withdrawal of medication used, catheter obstruction, or pump malfunction. Rarely patients may experience noise in the pump (when in high doses of infusion), pump translation (when the pump turns upside down - preventing replenishment), surgical wound opening (dehiscence) or skin necrosis. Talk about complications with your functional neurosurgeon before performing the procedure. Find out how he makes the pump refill and the usual frequency for it. For intraventricular route, the risks of a cerebral advent are comparable to ventriculo-peritoneal shunt puncture. The precision of catheter tip location requires neuronavigation systems to its placement, such as stereotaxy or neuronavigation. Some neurosurgeons also use neuroendoscopy for catheter placement.
The following link contains pictures of surgeries and procedures that can impress the visitor. Caution is recommended!
From what age can a baclofen pump be implanted?
The pump can be implanted in children from 3 years of age. Before definitive implantation of the baclofen pump, hospitalization is often necessary to perform the intrathecal baclofen test:How to test intrathecal baclofen?
What is the expected improvement with the baclofen pump?
Intrathecal infusion of baclofen dramatically decreases spasticity, especially in lower limbs, but also acts on lower limbs, with lower intensity. For ambulatory (walking) patients, the use of intrathecal baclofen should be performed with caution, as it may promote muscle relaxation that may hamper gait. Patients with dystonia may show a decrease in involuntary movements, as well as a global gain, with energy savings and consequent weight gain.
For more information, ask your functional neurosurgeon.
 |
|