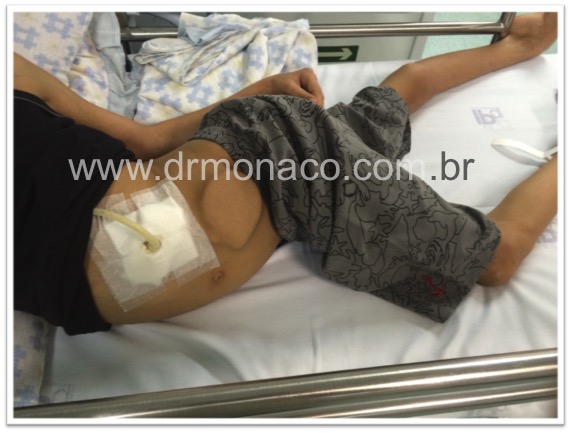
Pump Implant for Intrathecal Medications - Baclofen Pump
What is intrathecal drug infusion?
It is a neuromodulation method where a medication is injected continuously or intermittently directly into the cerebrospinal fluid (cerebrospinal fluid) around the spinal cord or into the brain. These medications are stored in reservoirs implanted in the body, which we call infusion pumps. They can be programmable with adjustable flows or continuous flow pumps. They are lodged beneath the skin in the subcutaneous tissue, and a catheter connects it to the fluid space where the medication is released directly.
The main drugs used in Intrathecal Infusion Pumps in Brazil are morphine and baclofen.

Which drugs are most used?
Morphine is the medication most commonly used for treatment of intractable chronic pain and baclofen for severe spasticity and painful spasms. The baclofen infusion pump can also be used to treat dystonias. Morphine also has an effect for the treatment of spasticity. The doses of intrathecal infusion medication are low (compared to oral ones), minimizing side effects and optimizing its therapeutic effect. Preoperative testing may be necessary. Other medications are also used in an infusion pump for the treatment of spasticity, in combination or not with baclofen, such as clonidine, bupivacaine, ziconotide, tizanidine, midazolam or hydromorphone, not all available in Brazil.
Oral baclofen did not work for me, so intrathecal baclofen is not good for me?
Oral baclofen has low absorption and arrives in very few doses where it should act, which is inside the CSF, for its action on the nervous system. If oral baclofen was not enough to improve its spasticity or the side effects were limiting, preventing oral dose increase, the intrathecal route could be tested as a therapeutic option, at the discretion of the functional neurosurgeon. Intrathecal baclofen trial is suggested prior to implantation of baclofen pump. Some cases do not require testing prior to pump implantation, such as spasticity secondary to spinal cord injury or multiple sclerosis, provided they have been responded to oral baclofen.
What is the difference between baclofen and intrathecal baclofen?
When an oral medication or by gastrostomy is used for it acts directly on the central nervous system, this medication must be absorbed in the digestive tract, fall into the bloodstream, cross the blood-brain barrier, and then be released into the cerebrospinal fluid, where it will reach its target of action. However, many medications go far beyond the blood-brain barrier, requiring high concentrations in the blood to achieve small concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid. With direct intrathecal infusion of baclofen, the concentrations reached in the CSF are much higher than the concentrations of the same medication even when used at the maximum oral dose. In the case of baclofen, it is estimated that its concentration around the marrow is 40 times greater than the maximum oral dose. If the doses were equivalent, ie the same oral dose was injected directly into the cerebrospinal fluid, the potency would be greater than 1000 times when the intrathecal route was used.
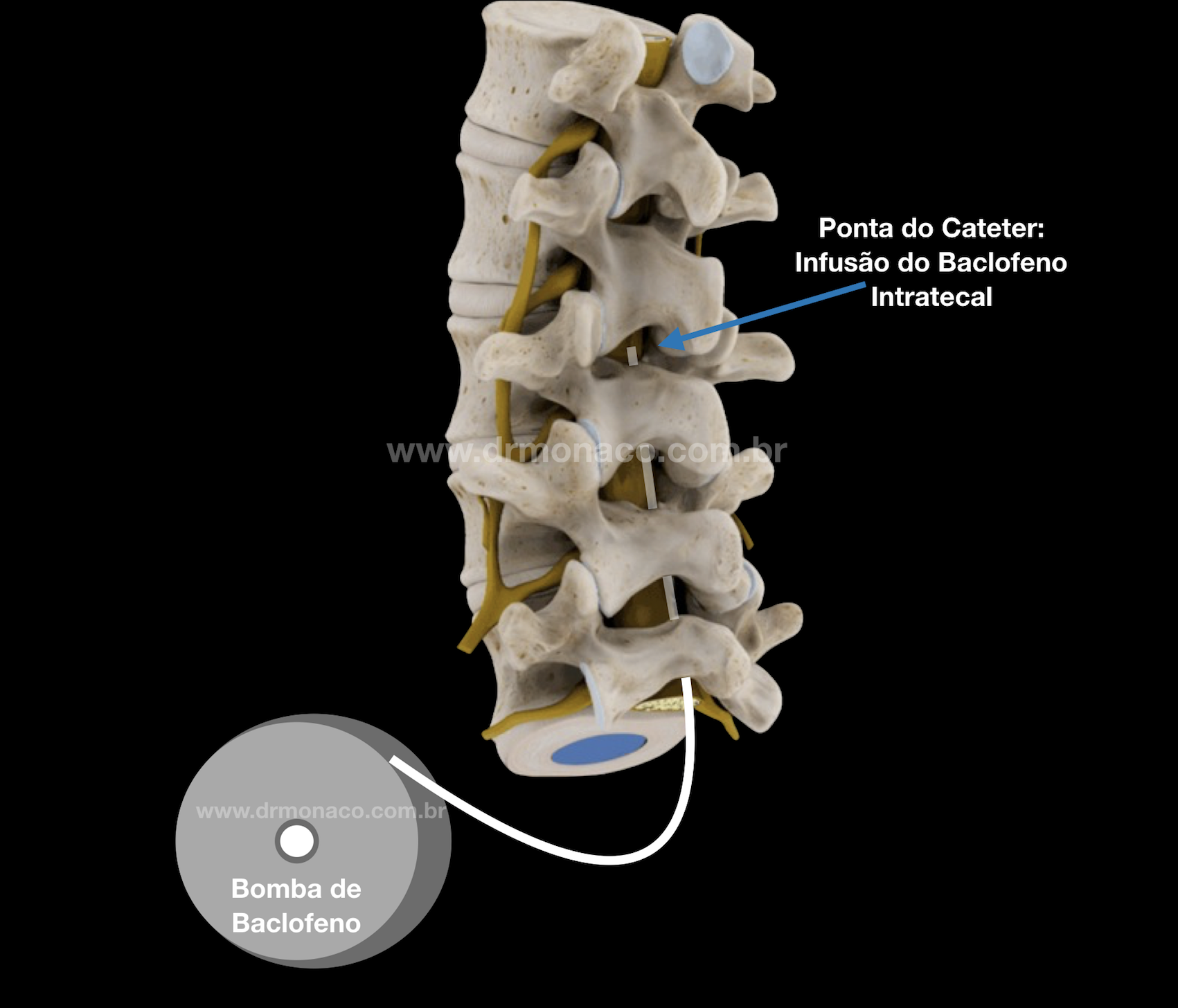
Intrathecal baclofen pump: The drug reservoir is usually implanted in the belly region, below the skin, and it leaves a catheter that takes the medication directly into the cerebrospinal fluid, distributing it in the central nervous system.
What care to take?
The pumps require some special care. The medication inside your tank should be temporarily replenished or replaced. This pump refill procedure (Refill - How to refill the medicine in the pump?) Is usually performed by puncturing the reservoir chamber through the skin without any anesthesia being necessary. The time interval for the refill varies depending on the medication used and the rate of infusion. Most medications lose their validity and pharmacochemical properties between 3 and 6 months stored in the implanted pumps, so it is necessary to replace the old medication with a new medication periodically. The electronic pumps have an internal battery, which when finished needs replacement. In this case, the pump is replaced by a new one, this occurs on average every 5 to 7 years depending on the use of the pump.
What infusion pumps are available in Brazil?
Currently we have only one model of electronic infusion pump programmable in Brazil, called Synchromed II, brand Medtronic. A competing electronic pump, called Prometra II of the Flowonix brand, is awaiting authorization from ANVISA to be distributed in the country. An option to electronic pumps are the gas-flow pumps, such as the German Tricumed, available in Brazil in adult and pediatric sizes. Since titration and mode of infusion of baclofen vary, the programmable electronic infusion pumps are best suited for infusion.
What are the complications of baclofen pump implant surgery?
The complications decrease in the hands of experienced teams, as well as their accomplishment in hospitals where the procedure is performed routinely. The most common complications are: infection, hematoma, postoperative pain, cerebrospinal fluid leakage (common in pediatric population), pump displacement, medication intoxication, abstinence from the medication used, catheter obstruction, or pump malfunction. Rarely patients may experience noise in the pump (when in high doses of infusion), pump translation (when the pump turns upside down - preventing replenishment), surgical wound opening (dehiscence) or skin necrosis. Talk about complications with your functional neurosurgeon before performing the procedure. Find out how he makes the pump refill and the usual frequency for it.
The following link contains pictures of surgeries and procedures that can impress the visitor. Caution is recommended!
From what age can a baclofen pump be implanted?
The pump can be implanted in children from 3 years of age. Before definitive implantation of the baclofen pump, hospitalization is often necessary to perform the intrathecal baclofen test:
How to test intrathecal baclofen?
What is the expected improvement with the baclofen pump?
Intrathecal infusion of baclofen dramatically decreases spasticity, especially in lower limbs, but also acts on lower limbs, with lower intensity. For ambulatory (walking) patients, the use of intrathecal baclofen should be exercised with caution, as it may promote muscle relaxation that may hamper gait. Patients with dystonia may show a decrease in involuntary movements, as well as a global gain, with energy savings and consequent weight gain. Intraventricular route is an option for dystonic patients.
For more information, ask your functional neurosurgeon.
 |
|